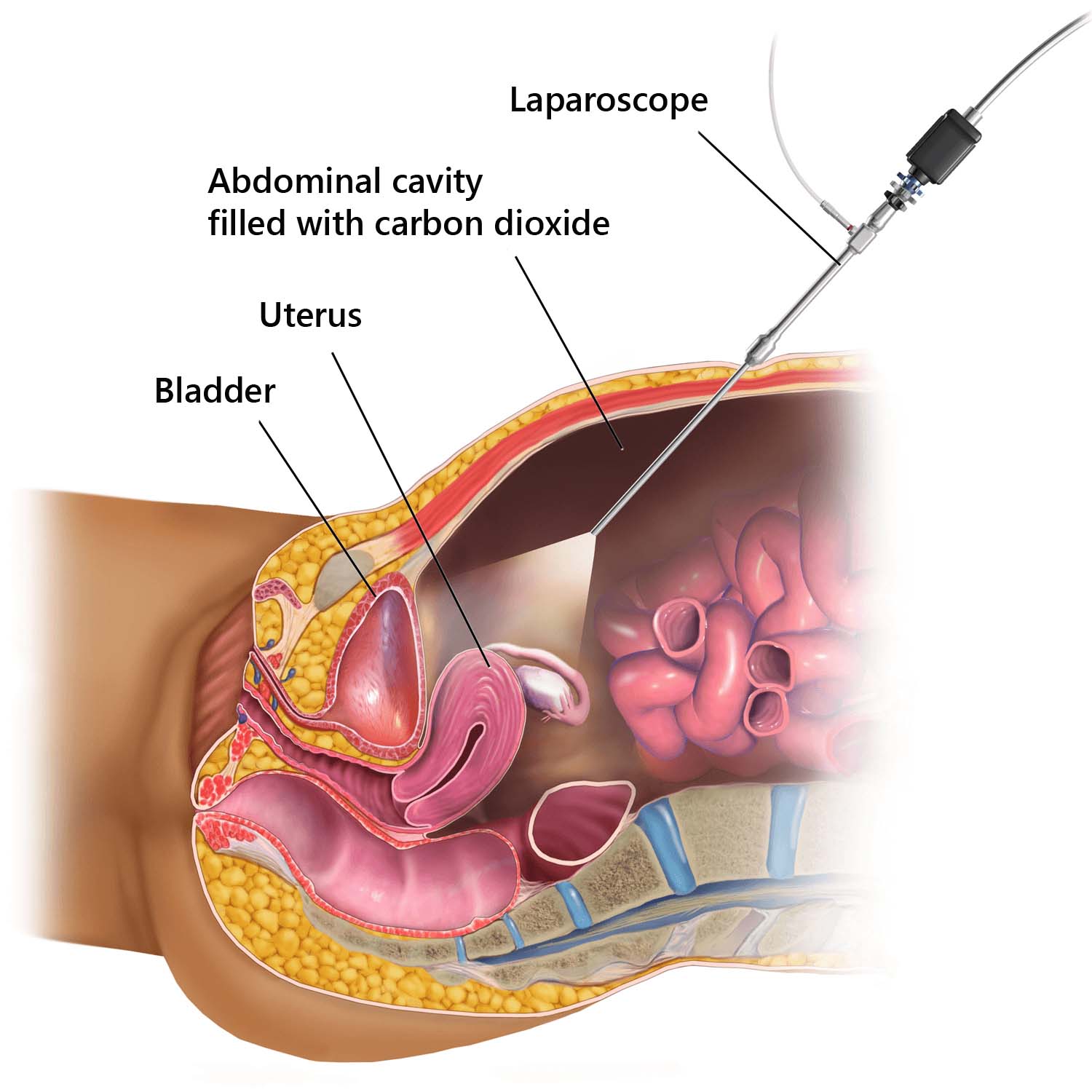
Diagnostic Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to view the internal organs of the abdomen to diagnose or treat conditions. A laparoscope, which is a small telescope with a light source, is inserted through a small incision to provide a clear view of the abdominal organs on a monitor.
Why is it performed?
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed to identify the causes of abdominal pain, to examine an abdominal mass, or to evaluate the extent of certain diseases such as cancer within the abdomen. It is also used to confirm conditions like appendicitis or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Potential Complications
Complications, although rare, can include bleeding, infection, or injury to abdominal organs. The procedure is typically safe with major complications being very rare.
Preparation and Procedure
Patients may need to undergo tests like ultrasound or CT scan before the procedure. Diagnostic laparoscopy is usually performed under general anesthesia but can also be done under local anesthesia with sedation. After the procedure, patients can usually go home the same day.

